Cotton as an important cash crop and cotton textile industry raw materials, with the increase of densely populated areas, cotton, grain and oilseed crops land competition problem is more and more serious, the use of cotton and grain intercropping can effectively alleviate the contradiction between the cultivation of cotton and grain crops, which can improve the productivity of the crop and the protection of ecological diversity and so on. Therefore, it is of great significance to quickly and accurately monitor the growth of cotton under intercropping mode.
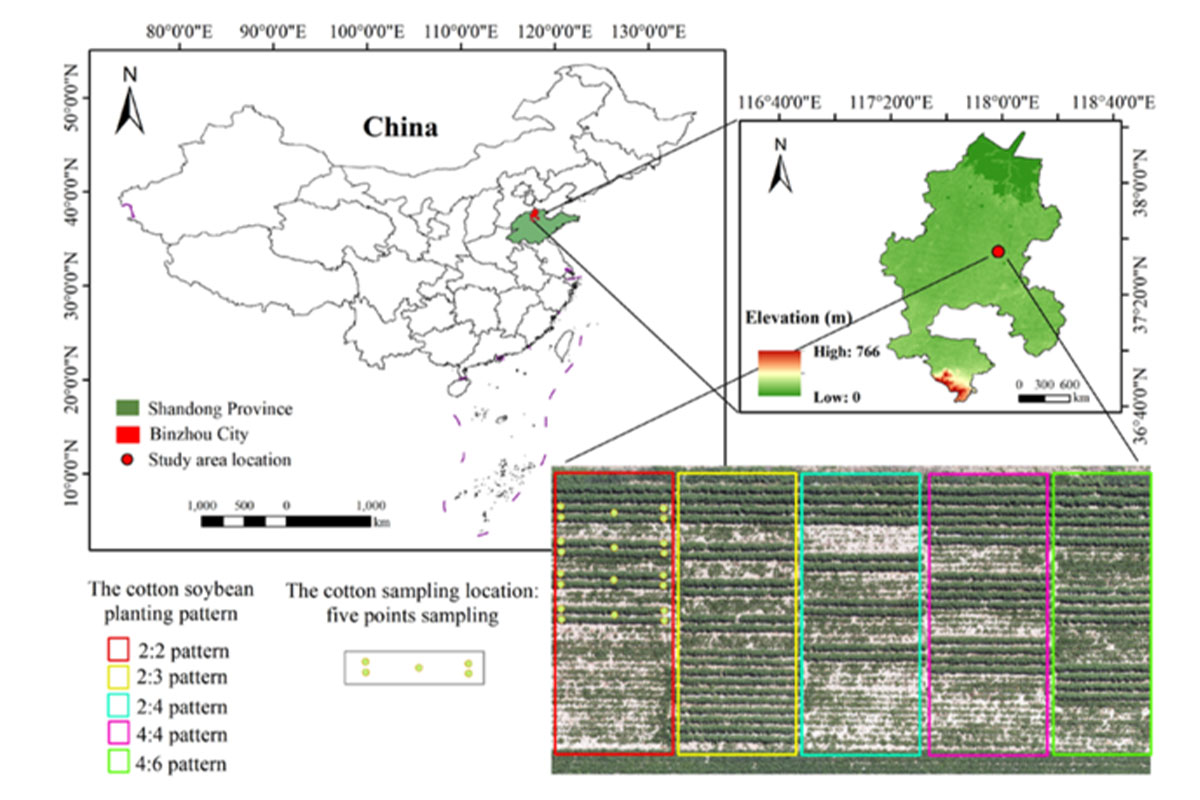
Multi-spectral and visible images of cotton at three fertility stages were acquired by UAV-mounted multi-spectral and RGB sensors, their spectral and image features were extracted, and combined with the height of cotton plants on the ground, the SPAD of cotton was estimated by voting regression integrated learning (VRE) and compared with three models, namely, Random Forest Regression (RFR), Gradient Boosted Tree Regression (GBR), and Support Vector Machine Regression (SVR). . We evaluated the estimation accuracy of different estimation models on the relative chlorophyll content of cotton, and analyzed the effects of different ratios of intercropping between cotton and soybean on the growth of cotton, so as to provide a basis for the selection of the ratio of intercropping between cotton and soybean and the high-precision estimation of cotton SPAD.
Compared with RFR, GBR, and SVR models, the VRE model showed the best estimation results in estimating cotton SPAD. Based on the VRE estimation model, the model with multispectral image features, visible image features, and plant height fusion as inputs had the highest accuracy with test set R2, RMSE, and RPD of 0.916, 1.481, and 3.53, respectively.
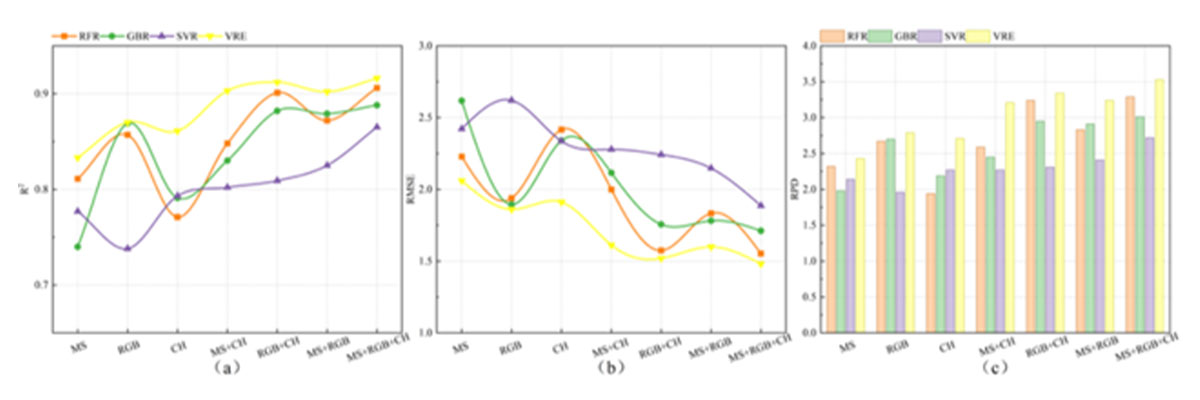
It was shown that multi-source data fusion combined with voting regression integration algorithm provides a new and effective method for SPAD estimation in cotton.
Post time: Dec-03-2024