1. Capacity (unit: Ah)

This is a parameter that everyone is more concerned about. Battery capacity is one of the important performance indicators to measure the performance of the battery, which indicates that under certain conditions (discharge rate, temperature, termination voltage, etc.) the battery discharges the amount of electricity (available JS-150D discharge test), that is, the capacity of the battery, usually in amperage - hours as a unit (abbreviation, expressed in A-H, 1A-h = 3600C). For example, if a battery is 48V200ah, it means that the battery can store 48V*200ah=9.6KWh, i.e., 9.6 kilowatts of electricity. Battery capacity is divided into actual capacity, theoretical capacity and rated capacity according to different conditions.
Actual capacity refers to the amount of electricity a battery can give under a certain discharge regime (a certain sedimentation level, a certain current density and a certain termination voltage). The actual capacity is generally not equal to the rated capacity, which is directly related to the temperature, humidity, charging and discharging rate. Generally, the actual capacity is smaller than the rated capacity, sometimes even much smaller than the rated capacity.
Theoretical capacity refers to the amount of electricity given by all the active substances participating in the battery reaction. That is, the capacity in the most ideal state.
Rated capacity refers to the nameplate indicated on the motor or electrical appliances in the rated operating conditions can continue to work for a long time capacity. Usually refers to apparent power for transformers, active power for motors, and apparent or reactive power for phase-regulating equipment, in VA, kVA, MVA. In application, the geometry of the pole plate, termination voltage, temperature, and discharge rate all have an impact on the battery capacity. For example, in the winter in the north, if a cell phone is used outdoors, the battery capacity will drop rapidly.
2. Energy Density (unit: Wh/kg or Wh/L)
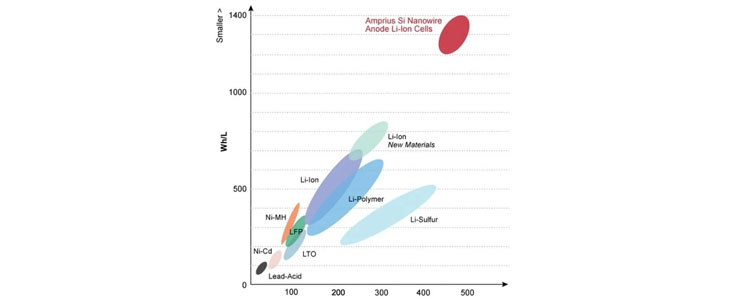
Energy density, battery energy density, for a given electrochemical energy storage device, the ratio of the energy that can be charged to the mass or volume of the storage medium. The former is called "mass energy density", the latter is called "volumetric energy density", the unit is respectively watt-hour/kg Wh/kg, watt-hour/liter Wh/L. The power here, is the above mentioned capacity (Ah) and the operating voltage (V) of the integral. When it comes to applications, the metric of energy density is more instructive than capacity.
Based on the current lithium-ion battery technology, the energy density level can be achieved at about 100~200Wh/kg, which is still relatively low and has become a bottleneck for lithium-ion battery applications in many occasions. This problem also occurs in the field of electric vehicles, in the volume and weight are subject to strict limitations, the energy density of the battery determines the maximum driving range of electric vehicles, so the "mileage anxiety" this unique term. If an electric vehicle's single driving range is to reach 500 kilometers (comparable to that of a conventional fuel vehicle), the energy density of the battery monomer must be 300Wh/kg or more.
The increase in energy density of lithium-ion batteries is a slow process, much lower than Moore's Law in the integrated circuit industry, which creates a differential between the performance improvement of electronic products and the energy density improvement of batteries that continues to widen over time.
Post time: Nov-10-2023